Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are essential components in electronics manufacturing. They provide a platform for connecting and supporting electronic components, allowing them to function as a cohesive unit. PCBs are used in various applications, from mobile phones and computers to medical devices and automotive systems. Understanding the manufacturing materials of PCBs is crucial in ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
- Basics of PCB Manufacturing Process
- Importance of Selecting the Right Materials for PCB Manufacturing
- Commonly Used Materials in PCB Manufacturing
- Understanding the Properties and Characteristics of PCB Materials
- Factors to Consider When Choosing PCB Materials
- Benefits of Using High-Quality PCB Materials
- Different Types of PCB Materials and Their Applications
- Challenges and Considerations in PCB Material Selection
Basics of PCB Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of PCBs involves several steps, from the design phase to the final assembly. The first step is designing the PCB layout using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Once the design is finalised, it is transferred to a copper-clad laminate material, which serves as the base for the PCB.
The next step is etching, where unwanted copper is removed using a chemical process, leaving behind the desired circuit pattern. After etching, the PCB goes through drilling, where holes are created for component placement. The final steps include plating, solder mask application, and surface finishing.
Importance of Selecting the Right Materials for PCB Manufacturing
Selecting suitable materials for PCB manufacturing is essential for several reasons. Firstly, the choice of materials directly impacts the electrical performance and reliability of the PCB. Different materials have varying dielectric properties, thermal conductivity, and electrical resistance, which can affect signal integrity and overall functionality.
Secondly, the materials used in PCB manufacturing determine the mechanical strength and durability of the board. The PCB should withstand environmental factors such as temperature variations, humidity, and vibrations. Lastly, selecting high-quality materials ensures the longevity of the PCB and reduces the risk of failure or malfunction.
Commonly Used Materials in PCB Manufacturing
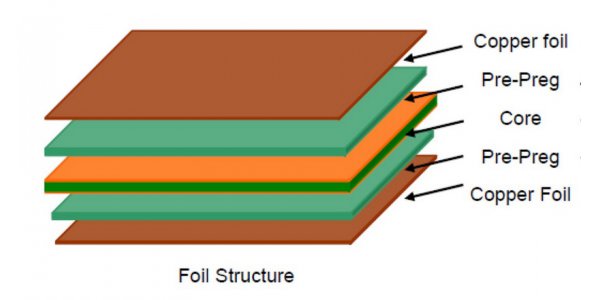
Several materials are commonly used in PCB manufacturing, each with its unique properties and benefits. The most widely used material is FR-4, a flame-resistant glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. FR-4 is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties, mechanical strength, and affordability.
Another commonly used material is flexible polyimide, ideal for applications requiring flexibility, such as wearable devices and aerospace systems. Other materials include ceramic, metalcore, and high-frequency laminates, each suitable for specific applications based on their thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, and signal integrity requirements.
Understanding the Properties and Characteristics of PCB Materials
It is essential to understand the properties and characteristics of different materials to select suitable materials for PCB manufacturing. A material’s dielectric constant, or relative permittivity, determines its ability to store electrical energy. To minimise signal loss, materials with lower dielectric constants are preferred for high-frequency applications.
Thermal conductivity is another important property, especially for applications that generate a lot of heat. High thermal conductivity materials help dissipate heat efficiently, preventing component damage. Other properties to consider include electrical resistance, water absorption, and coefficient of thermal expansion.
Factors to Consider When Choosing PCB Materials
When choosing PCB materials, several factors need to be considered. Firstly, the intended application and operating conditions play a significant role. Different applications have different requirements regarding electrical performance, thermal management, and mechanical strength. Secondly, the cost-effectiveness of the materials should be evaluated.
While high-end materials may offer superior performance, they might not be economically viable for specific applications. Additionally, the availability and compatibility of the materials with existing manufacturing processes should be considered. Lastly, the reliability and track record of the materials and suppliers should be considered to ensure consistent quality and availability.
Benefits of Using High-Quality PCB Materials
Using high-quality PCB materials offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it enhances the overall performance and reliability of the PCB. High-quality materials provide better electrical insulation, thermal management, and mechanical strength, resulting in improved signal integrity and reduced risk of failure.
Secondly, high-quality materials offer better longevity, ensuring that the PCB can withstand harsh environments and operate consistently over an extended period. Moreover, high-quality materials often have better manufacturing tolerances, allowing for more precise and efficient assembly processes.
Finally, using high-quality materials can enhance the reputation and credibility of the manufacturer, as it demonstrates a commitment to delivering reliable and high-performance electronic products.
Different Types of PCB Materials and Their Applications
Different types of PCB materials are available, each designed for specific applications. FR-4 is the most commonly used material due to its versatility and affordability. It is suitable for various applications, from consumer electronics to industrial equipment.
Flexible polyimide is used in applications that require flexibility, such as medical devices and automotive systems. Ceramic PCBs are ideal for high-power applications that generate heat, such as power amplifiers and LED lighting.
Metal core PCBs are used for applications that require efficient thermal management, like high-power LEDs and power converters. High-frequency laminates, such as Rogers materials, are used in RF and microwave applications that require excellent signal integrity.
Challenges and Considerations in PCB Material Selection
While selecting PCB materials, there are several challenges and considerations to remember. One challenge is the continuous advancement of technology, which leads to the need for materials with higher performance capabilities. Keeping up with these advancements and selecting materials that meet future requirements can be challenging.
Another consideration is the environmental impact of the materials used. Manufacturers should strive to choose environmentally friendly materials and comply with regulations. Additionally, the compatibility of the materials with existing manufacturing processes and equipment should be evaluated to ensure a smooth production flow. Lastly, the cost-effectiveness of the materials should be balanced with the desired performance, reliability, and longevity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting suitable materials for PCB manufacturing is critical in ensuring electronic device performance, reliability, and longevity. The choice of materials directly impacts the electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties of the PCB and its ability to withstand harsh environments. Understanding the properties and characteristics of different materials is essential for making informed decisions.
Factors such as the intended application, cost-effectiveness, availability, and the benefits of using high-quality materials should be considered. By carefully selecting the right materials and considering the challenges and considerations, manufacturers can create PCBs that meet the requirements of various applications and deliver reliable and high-performance electronic products.