How to Determine Landscape Measurements [Full Guide]
Precise measurements are essential for successful landscape design. This is because size is a foundational element, directly impacting the overall aesthetic and functionality of the landscape. Precisely measured dimensions ensure your design plan adapts to real-world conditions, meets intended uses, and creates a visually pleasing and well-coordinated landscape.
On the contrary, inaccurate measurements in design drawings can lead to unnecessary material waste, project delays, cost overruns, and even safety risks. Therefore, it is important for landscape designers to prioritize accuracy in accurate landscape measurements throughout the process, making use of professional measurement tools and software to guarantee precise design results. In this article, we will provide you with a detailed guide on how to determine landscape measurements accurately.
What Do You Need to Prepare Before Landscape Measurements
To begin with, it is necessary to make sufficient preparations to ensure accurate dimensional data and spatial information can be provided for landscape design. Now, let’s go through what you need to prepare before landscape measurements.
Site Survey
Conducting a thorough site survey is a crucial first step in any landscaping project. It serves as the foundation for designers to comprehend the project’s conditions and acts as the starting point for the design plan. Moreover, it offers precise guidance and a groundwork for subsequent measurement tasks. The survey involves gathering and analyzing data on various aspects of the landscape site, including:
- Terrain features: elevation, slope, geological structure, soil type, etc.
- Land distribution: roads, trees, flowers, etc.
- Surrounding buildings: location, size, shape, material, etc.
- Plant conditions: types, quantity, location, height, crown width, etc.
- Waterbody distribution: area, depth, water level, water quality, etc.
Visual inspection is a common and effective method for initially understanding the overall landscape site condition. However, meticulous note-taking and recording of measurements are crucial to ensure accurate data capture. Additionally, photography is another valuable tool, allowing for efficient documentation of topography, hydrology, climate, surrounding environment, and other relevant aspects of the project site. Furthermore, technologies like aerial photography and satellite remote sensing offer alternative methods for collecting landscape image data, potentially streamlining the site analysis and processing stages.
Measurement Tools
To conduct precise landscape measurements, it is essential to have the appropriate measurement tools. Here are some crucial instruments to think about:
- Precise Measuring Instruments: Total stations or other high-precision tools provide accurate ground elevation, coordinate, and distance data for site measurement.
- Distance Meter: It is used to measure long distances to help determine the size and range of the site.
- Level and Inclinometer: These tools measure height differences and determine the ground slope, which is vital for terrain analysis and design adjustments.
- Data Recording Tools: A notebook and pen or a digital device are essential for recording field measurements accurately and promptly.
- Camera: Take photos to document landscape features and current conditions to provide a visual reference for the design team.
- Marking Tools: They help to mark measurement points and boundaries to ensure the accuracy and consistency of measurement data.
- Landscape Design Software: It provides various measuring tools to improve measurement efficiency, accuracy, and data management efficiency, providing accurate data and information for landscape design.
- By fully preparing these tools and performing a site survey, you can lay a solid foundation for landscape surveying and ensure that the resulting data is accurate and reliable to support subsequent landscape design work.
3 Methods You Can Use to Measure Up the Landscape
After preparing the required tools, let’s move to this part to access 3 commonly used methods to measure up the landscape accurately.
Method 1. Direct Line Measurement
Line measurement is a widely utilized method in landscape surveying, which can quickly and accurately measure the determine the distance between two points. It’s well-suited for measuring relatively long and straight lines within landscapes, such as roads, rivers, building edges, and green belts. In addition, when using line measurement, it is advisable to choose areas with relatively flat terrain and minimal obstructions as much as possible, which can reduce measurement errors.
To begin, clearly mark both the starting and ending points of your measurement using visible markers. Then, utilize a suitable tool like a tape measure, theodolite, laser rangefinder, or other appropriate instrument to measure the distance between the marked points. Following this, document the outcomes of the line measurement, encompassing both distance and direction for for future reference and analysis.
Method 2. Running Measurement
This method is similar to line measurement, which measures the distance between points. However, instead of stopping at each point, continuous measurement captures distance continuously along a line or area. This makes continuous measurement more appropriate for features with complex geometries, such as curved lines or irregular areas, where direct point-to-point measurements may not be feasible, helping to determine parameters like area, perimeter, and side length for such features.
Similar to line measurement, identifying and marking the starting and ending points of the line or area is essential. You can then use a pedometer, wheel odometer, or GPS device to continuously measure distance as you walk or run along the trail. This method is faster than line measurement, but less accurate, especially on uneven terrain. Therefore, this method is best used to get a general idea of the landscape’s size rather than performing precise measurements.
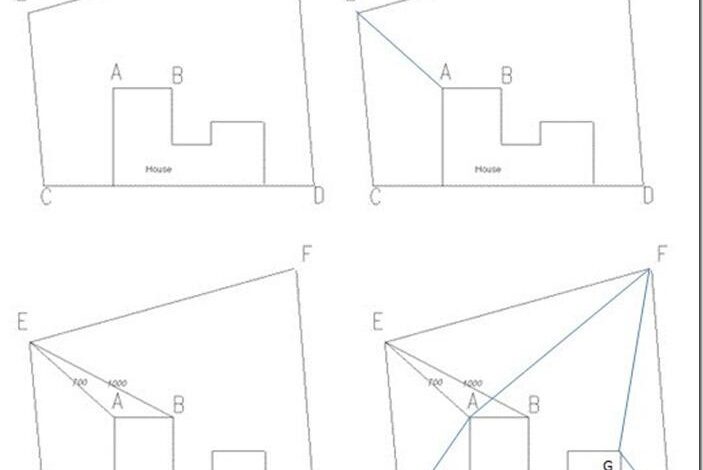
Method 3. Triangulation
Triangulation is a measurement technique that leverages the geometric relationships within triangles to determine the lengths and angles of their sides. This method is particularly suited for situations where cannot be directly assessed, such as in complex terrain, large structures, or areas with significant height variations. It relies on the geometric principles of triangles and deduces the length or position of the target segment or area by measuring known segments and angles. While triangulation offers high-precision results, it demands proper skill and experience.
To begin, selecting suitable measurement points is crucial, ensuring visibility and optimal positioning for accurate readings. Subsequently, use a goniometer or other appropriate instruments to measure edges and angles. Besides, maintaining instrument stability throughout the process is crucial as it directly impacts accuracy. Following this, the other sides and angles of the triangle can be calculated based on the shape principles of a triangle.
Method 4. Offsets
Offset measurement is a method for determining the spatial position of a point by measuring its horizontal distance and height difference from a known reference point. This method is considered simple, convenient, and effective, finding widespread applications in landscape measurements, particularly in areas with significant terrain undulations or areas with dense buildings. By setting reference points and measuring along the reference line, accurate terrain data can be obtained through offset measurement, thereby avoiding issues associated with traditional methods such as the need for numerous control points, a high measurement workload, and elevated costs.
When using the offset measurement method, the reference point should be set close to the measured point and in a stable position. Then, use measuring instruments such as theodolite and level to determine the horizontal distance and height difference between the reference point and the measured point. Then the accurate data of the measurement area can be calculated based on the measurement results.
Other Helpful Tips to Determine Landscape Measurements
In addition to the measurement methods mentioned above, many practical tips can help you determine landscape measurements. for example:
- Draw a Scaled Sketch
Creating a scale sketch is an effective method to determine the scope and accuracy of landscape measurements. Design plans can be hand-drawn on paper or created using professional landscape design software. Both methods allow you to record the dimensions of key elements. This can guide your actual measurements and provide a useful framework for further design development. While professional landscape design software offers advanced features, it may involve higher costs. Consider starting with inexpensive CAD software such as ZWCAD first to assess your needs before making a decision.
- Ask for a Deed Map
If the landscape measurements involve a house or land, you can request a house or land purchase deed from the relevant department. Key information such as the size, boundaries, and shape of the land are usually marked on the deed map, which can be used as a reference for landscape measurements.
- Measure Critical Slope
If there are hardscapes in the landscape, such as roads, buildings, pools, etc., the critical slope of these hardscapes needs to be measured. Critical slope refers to the maximum slope allowed for the hardscape when designing. Measuring critical slopes can help you avoid safety hazards.
Conclusion
By following these options, you can easily ensure accurate and appropriate measurements, which will serve as a solid foundation for creating a satisfactory landscape and provide strong support for subsequent landscape management work. Hope this article helps you and please feel free to share it.




